Giáo án ôn thi THPT quốc gia môn Tiếng Anh năm 2015 - 2016 - Chuyên đề 1 đến chuyên đề 3
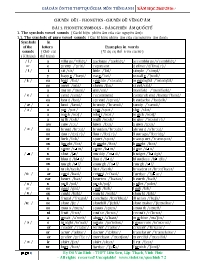
BÀI 1. PHONETIC SYMBOLS - BẢNG PHIÊN ÂM QUỐC TẾ
1. The symbols vowel sounds (Các kí hiệu phiên âm của các nguyên âm):
1.1. The symbols of pure vowel sounds (Các kí hiệu phiên âm của các nguyên âm đơn):
Symbols of the sounds
(Kí hiệu) In
letters
(Chữ cái
thể hiện)
Examples in words
(Ví dụ cụ thể trên các từ)
/ І /
or
/ i / a village /’vilidʒ/ package /’pækidʒ/ assemblage /ә’semblidʒ/
e pretty /’priti/ represent deliver /di’livә(r)/
i sit /sit/ little /’litl/ simple /’simpl/
y happy /’hæpi/ easy /’i:zi/ usually /’ju:ʊli/
/ i: / ea lead /li:d/ seaside /’si:said/ meaningful /’mi:niŋfʊl/
ee meet /mi:t/ sheep /ʃi:p/ steel /sti:l/
/ e / a many /’meni/ any/eni/ manifold /’menifәʊld/
e send /send/ recommend comprehend /kәmpri’hend/
ea head /hed/ spread /spred/ headache /‘hedeik/
CHUYÊN ĐỀ I – PHONETICS - CHUYÊN ĐỀ VỀ NGỮ ÂM BÀI 1. PHONETIC SYMBOLS - BẢNG PHIÊN ÂM QUỐC TẾ 1. The symbols vowel sounds (Các kí hiệu phiên âm của các nguyên âm): 1.1. The symbols of pure vowel sounds (Các kí hiệu phiên âm của các nguyên âm đơn): Symbols of the sounds (Kí hiệu) In letters (Chữ cái thể hiện) Examples in words (Ví dụ cụ thể trên các từ) / І / or / i / a village /’vilidʒ/ package /’pækidʒ/ assemblage /ә’semblidʒ/ e pretty /’priti/ represent deliver /di’livә(r)/ i sit /sit/ little /’litl/ simple /’simpl/ y happy /’hæpi/ easy /’i:zi/ usually /’ju:ʊli/ / i: / ea lead /li:d/ seaside /’si:said/ meaningful /’mi:niŋfʊl/ ee meet /mi:t/ sheep /ʃi:p/ steel /sti:l/ / e / a many /’meni/ any/eni/ manifold /’menifәʊld/ e send /send/ recommend comprehend /kәmpri’hend/ ea head /hed/ spread /spred/ headache /‘hedeik/ / æ / a land /lænd/ brandy /’brændi/ sandy /’sændi/ / ɔ / o pot /pɔt / spot /spɔt / slot /slɔt / a wash /wɔʃ / what /wɔt / watch /wɔtʃ/ / ɔ: / a talk /tɔ:k/ walk /wɔ:k/ water /’wɔ:tә(r)/ aw saw /sɔ:/ lawn /lɔ:n/ pawn /pɔ:n/ oa broad /brɔ:d/ broaden/’brɔ:dn/ abroad /ә’brɔ:d/ oo door /dɔ:(r)/ floor /flɔ:(r)/ floorage /’flɔ:ridʒ/ or fork /fɔ:k/ sport /spɔ:t/ transport /’trænspɔ:t/ ou fought /fɔ:t/ thought /θɔ:t/ bought /bɔ:t/ / L / o some /sLm/ come /kLm/ done /dLn/ u shut /ʃLt/ muddy /’mLdi/ budget /’bLdʒit/ oo blood /blLd/ flood /flLd/ bloodless /blLdlis/ ou tough /tLf/ enough /i’nLf/ rough /rLf/ / ɑ: / a task /ta:sk/ fast /fa:stk/ broadcast /br ɔ:d’ka:st/ ar card /ka:d/ retard /ri’ta:d/ farther /’fa:dәr/ ear heart /ha:t/ hearten /’ha:tәn/ hearth /ha:θ/ / ʊ / or / u / u pull /pʊl/ push /pʊʃ/ pullet /’pʊlet/ oo good /gʊd/ cook /kʊk/ look /lʊk/ ou could /kʊld/ would /wʊld/ should /ʃʊld/ / u: / u frugal /’fru:gәl/ conclude /kɔn’klu:d/ illusion /i’lu:ʃn/ oe shoe /ʃu: / shoebill /’ʃu:bil/ shoemaker /’ʃu:meikәr/ oo moon /mu:n/ spoon /spu:n/ smooth /smu:θ/ ui fruit /fru:t/ cruise /kru:s/ recruit /ri’kru:t/ / ә / a await /ә’weit/ about /ә’baut/ machine /mә’ʃi:n/ o tonight /tә’nait/ potato /pә’teitәu/ tomorrow /tә’mɔrәʊ/ er reader /’ri:dәr/ writer /’raitәr/ cruiser /’kru:sәr/ or actor /’æktәr/ doctor /’dɔktәr/ translator /’trænsleitәr/ / з: / er prefer /pri’fз: r/ merchant /’mз:tʃәnt/ merciful /’mз:sifʊl/ ir shirt /ʃз:t/ skirt /skз:t/ first /fз:st/ ur hurt /hз:t/ further /’ʃз:dә/ furnish /’ʃз:niʃ/ or word /wз:d/ work /wз:k/ worm /wз:m/ ear heard /hз:d/ earth /з:θ/ earthen /’з:θәn/ 1. 2. The diphthongs and triphthongs (Các kí hiệu phiên âm của các nguyên đôi, ba): Symbols of the sounds (Kí hiệu) In letters (Chữ cái thể hiện) Examples in words (Ví dụ cụ thể trên các từ) / ei / a case /keis/ baby /beibi/ lazy /leizi/ ai maid /meid/ maiden /’meidn/ maidenly /’meidnli/ ay say /sei/ clay /klei/ play /plei/ ei eight eighthly /’eiθli/ eiranic /ei’rænik/ / ai / i kite /kait/ night /nait/ mine /main/ y sky /skai/ fly /flai/ satisfy /’sætisfai/ / ɔi / oi soil /sɔil/ coin /kɔin/ spoil /spɔil/ oy employ /im’plɔi/ enjoy /ii’dʒɔi/ employment /im’plɔimnt/ / aʊ / ou mouse /maʊs/ mouth /maʊθ/ surround /sз:’raʊnd/ ow now /naʊ/ power /’paʊ әr/ cowboy /’kaʊ bɔi/ / әʊ / o cold /kәʊld/ scold /skәʊld/ fold /fәʊld/ ow slow /slәʊ/ flow /flәʊ/ show /ʃәʊ/ ew sew /sәʊ/ sewing /sәʊiŋ/ sewn /sәʊn/ / iә / ear hear /hiә(r)/ fear /fiә(r)/ near /niә(r)/ ere here /hiә(r)/ merely /’miәli/ atmosphere /’ætmɔsfiә(r)/ / eә / ere there /deә(r)/ therapy /’θeәrәpi/ thereabout /’deәrәbaʊt/ are fare /feә(r)/ share /ʃeә(r)/ stare /steә(r)/ air hair /heә(r)/ fair /feә(r)/ stairs /steә(r)s/ / ʊә / our tour /tʊә(r)/ tourer /tʊәrә/ tourism /’tʊәrizm/ / aiә / ire tire /taiә/ fire /faiә/ firemen /’faiәmen/ yre tyre /taiә/ tyreles /’taiәlis/ tyre-pump /’taiә pLmp/ yer buyer /baiә/ flyer /flaiә/ buyer /baiә/ / әʊә / ower slower /slәʊә/ slower /slәʊә/ slower /slәʊә/ / aʊә / ower shower /ʃaʊә/ power /paʊә/ flower /flaʊә/ our flour /flaʊә/ sour /saʊә/ flour /flaʊә/ / eiә / ayer prayer /preiә/ player /pleiә/ sprayer /spreiә/ eyer greyer /greiә/ greyer /greiә/ greyer /greiә/ / ɔiә / oyer enjoyer /in’dʒɔiә/ enjoyer /in’dʒɔiә/ employer /im’plɔiә/ oyal loyal loyalty /’lɔiәlti/ loyal /’lɔiәl/ 2. The symbols of the consonant sounds (Các kí hiệu phiên âm của các phụ âm): 2.1. The symbols of voiceless consonants (Kí hiệu phiên âm của các phụ âm vô thanh): Symbols of the sounds (Kí hiệu) In letters (Chữ cái thể hiện) Examples in words (Ví dụ cụ thể trên các từ) / p / p pen /pen/ paint /peint/ people /’pi:pәl/ / f / f five /faiv/ formal /’fɔ:mәl/ family /’fæmili/ ph physics /’fiziks/ physician /fi’ziʃn/ physical /fi’zikәl/ gh laugh /la:f/ enough /i’nLf/ rough /rLf/ / q / th throw /θrәʊ/ thunder /’θLndә(r)/ sixth /siksθ/ / t / t teach /ti:tʃ/ temple /’tempәl/ tittle /’taitәl/ ed looked /lʊkt/ laughed /la:ft/ stopped /stɔpt/ / s / s site /sait/ sandy /’sændi/ sample /’sæmpәl/ c centre /’sentә/ century /’sentʃʊri/ cell /sel/ / ʃ / sh sheep /ʃi:p/ sheet /ʃi:t/ English /’iŋliʃ/ ch machine chaise /ʃeiz/ champagne /ʃæm’pein/ s sugar /’ʃʊgә/ sugary /’ʃʊgәri/ sure /’ʃʊә(r)/ / t∫ / ch choice /tʃɔis/ church /tʃз:tʃ/ chimney /’tʃimni/ t fixture /'fikst∫ә/ future / 'fju:t∫ә/ question / 'kwest∫n/ / k / k kitchen kiss /kis/ king /kiŋ/ c concert /kɔn’sз:t/ cancel /’kænsәl/ comedy /’kLmedi/ ch chemist /’kemist/ chemistry /’kemistri/ chemical /’kemikәl/ q quite /kwait/ question / 'kwest∫n/ conquest /’kɔŋkwest/ / h / h hike /haik/ hunger /’hLŋgә(r)/ homeless /’hәʊmlis/ wh whoop /hu:p/ whose /hu:z/ wholesale /’hɔʊlseil/ 2.2. The symbols of voiced consonants (Kí hiệu phiên âm của các phụ âm hữu thanh): Symbols of the sounds (Kí hiệu) In letters (Chữ cái thể hiện) Examples in words (Ví dụ cụ thể trên các từ) / b / b boy /bɔi/ bamboo /bæm’bu:/ band /bænd/ / v / v visit /vizit/ van /væn/ victory /vlktәri/ f of /әv/ of /әv/ of /әv/ / d / th them /dәm/ with /wid/ though /dәʊ/ / d / d done /dLn/ doctor /’dɔktә(r)/ dancer /dænsә(r)/ ed lived /livd/ earned /з:nd/ cancelled /’kænsәld/ / z / z zebra /zi:brә/ zip /zip/ zealot /’zelәt/ s visit /’vizit/ visual /’vizjʊәl/ teachers /ti:tʃәz/ / ʒ / s vision /’viʒn/ usual /’jʊʒʊәl/ usually /’jʊʒʊәli/ / dʒ / g germ /dʒз:m/ gene /dʒi:n/ age /eidʒ/ j jam /dʒæm/ jam /dʒæz/ joyful /dʒɔifʊl/ / g / g gift /gift/ gain /gein/ girl /gз:l/ / l / l little /’litәl/ lamp /læmp/ light /lait/ / m / m monk /mɔŋk/ mammal /’mæmәl/ Monday /’mLndei/ / n / n name /neim/ number /nLmbә/ noise /nɔis/ / ŋ / n think /θiŋk/ thank /θæŋk/ sink /siŋk/ ng sing /siŋ/ thing /θiŋ/ ceiling /’si:liŋ/ / r / r rural /’rʊәrәl/ ring /riŋ/ reader /’ri:dә/ / w / w with /wid/ wine /wain/ wing /wiŋ/ wh when whistle /’wisәl/ whisper /’wispә/ / j / y young /jLŋ/ yearly /’jiәli/ youth /ju:θ/ u music /’mju:sik/ unit /’ju:nit/ university /ju:ni’v з:siti/ / ф / mute cases h honest /’ɔ:nist/ hour /aʊә/ heir /aiә/ k knight /nait/ knit /nit/ known /nɔʊn/ b comb /kɔʊm/ climb /klaim/ debt /det/ p pneumonia /njʊ’mɔ:niә/ psychology /sai’kɔ:lɔdʒi/ psychiatrist /sai’kiәtrist/ BÀI 2. EXERCISES ON PHONETIC SYMBOLS BÀI TẬP NHẬN BIẾT ÂM Exercise 1: Find the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently from the others of the same group. A. candy B. sandy C. many D. handy A. earning B. learning C. searching D. clearing A. pays B. stays C. says D. plays A. given B. risen C. ridden D. whiten A. cough B. tough C. rough D. enough A. accident B. jazz C. stamp D. watch A. this B. thick C. maths D. thin A. gas B. gain C. germ D. good A. bought B. naught C. plough D. thought A. forks B. tables C. beds D. windows A. handed B. booked C. translated D. visited A. car B. coach C. century D. cooperate A. within B. without C. clothing D. strengthen A. has B. bag C. dad D. made A. kites B. catches C. oranges D. buzzes A. student B. stupid C. study D. studio A. wealth B. cloth C. with D. marathon A. brilliant B. trip C. tripe D. tip A. surgeon B. agent C. engine D. regard A. feather B. leather C. feature D. measure Exercise 2: Find the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently from the others of the same group. A. geology B. psychology C. classify D. photography A. idiom B. ideal C. item D. identical A. children B. child C. mild D. wild A. both B. myth C. with D. sixth A. helped B. booked C. hoped D. waited A. name B. natural C. native D. nation A. blood B. food C. moon D. pool A. comb B. plumb C. climb D. disturb A. thick B. though C. thank D. think A. flour B. hour C. pour D. sour A. dictation B. repetition C. station D. question A. dew B. knew C. sew D. few A. asked B. helped C. kissed D. played A. smells B. cuts C. opens D. plays A. decided B. hatred C. sacred D. warned A. head B. break C. bread D. breath A. blood B. tool C. moon D. spool A. height B. fine C. tidy D. cliff A. through B. them C. threaten D. thunder A. fought B. country C. bought D. ought CHUYÊN ĐỀ II – SENTENCE BUILDING - CHUYÊN ĐỀ VỀ VIẾT LẠI CÂU BÀI 3. SENTENCE BUILDING - VIẾT LẠI CÂU I. Introduction: Trong tiếng Anh, cũng như nhiều ngôn ngưc khác, ta có thể dùng nhiều cấu trúc lời nói khác nhau để diễn đạt cùng một ý, hay một lời nói. Nói cách khác một câu nói không đơn thuần chỉ có ý nghĩa duy nhất theo một cấu trúc ngữ pháp, mà câu nói ấy có thể được truyền tải theo một hình thức cấu trúc ngữ pháp khác nào đó mà vẫn giữ nguyên được ý nghĩa gốc của nó. Hình thức viết lại câu (sentence transformation) chính là hình thức viết lại một câu cho trước bằng một cấu trúc mới nhưng không làm thay đổi ý nghĩa ban đầu của câu ấy. Ví dụ như: Câu gốc: He has lived here since 1990. (the present perfect tense) Câu viết lại: He moved here in 1990. (the simple past tense) → Chuyển đổi câu sử dụng thì của động từ, động từ thay thế và trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian. Câu gốc: We can find him nowhere. (affirmative sentence) Câu viết lại: Nowhere can we find him. (inversion sentence) → Chuyển đổi câu sử dụng hình thức đảo ngữ (inversion) để nhấn mạnh. Câu gốc: She is the most intelligent student in my class. (superlative degree) Câu viết lại: No one in my class is as intelligent as she is. (negative positive degree) → Chuyển đổi câu sử dụng các hình thức so sánh với một tính từ. Câu gốc: “Don’t touch the wire, boys!” said Mr. Hung. (direct speech) Câu viết lại: Mr. Hung told the boys not to touch the wire. (indirect speech) → Chuyển đổi câu sử dụng cách chuyển từ câu trực tiếp sang câu gián tiếp. II. Some transformative for ... điểm cao hoặc điểm tuyệt đối cho phần này nếu học sinh nắm chắc kĩ năng tổ chúc ý tưởng, vận dụng kiến thức, thực hiện tốt các bước xây dựng dàn ý và viết bài. Bài này trình bày các thủ thuật viết đoạn văn và giới thiệu một số đề luyện tập, bài viết mẫu để các em tham khảo. Và cũng để đề phòng yêu cầu mới, những đòi hỏi cao hơn về phần viết luận trong đề thi, phần viết bài luận và các bài viết mẫu cũng được giới thiệu ở phần cuối của bài này. I. What is a paragraph? Thế nào là một đoạn văn? 1. Definitions: Định nghĩa - Một đoạn văn là một loạt câu phát triển, ủng hộ, chứng minh một ý nào đó, và ý này thường là câu chủ đề (topic sentence) của đoạn văn. Các câu còn lại (supporting sentences) phát triển, giải thích, minh họa cho câu chủ đề. Câu kết luận (concluding sentence) của đoạn văn là câu khẳng định lại câu chủ điểm, tóm tắt lại các ý chính của đoạn văn. - A paragraph is a group of sentences that deal with a single topic with the length (as required in the GCSE) of around 150 words. Đoạn văn trong tiếng Anh là một tổ hợp câu với độ dài (yêu cầu thi THPT Quốc Gia) chừng 150 từ, diễn tả hay bàn thảo về một chủ đề nhất định. - Normally (but not always), the first sentence introduces the topic. Other sentences give the definitions, examples, information, reasons, restatements, and summaries. Thông thường (không phải là luôn luôn), câu đầu tiên diễn tả chủ đề. Các câu còn lại là sự giải trình, dẫn chững, tái khảng định, thêm thông tin và tóm lược. - The parts of the paragraph are linked together by the phrases and conjunctions. They guide the readers through the argument presented. Xuyên suốt đoạn văn, các cụm từ, liên từ được sử dụng để kết nối và dẫn dắt độc giả theo chủ đề được bàn thảo. 2. Parts of a Paragraph: Các phần của đoạn văn 2.1. Topic Sentence: Câu chủ đề - đưa ra chủ đề để bàn thảo 2.2. Supporting Details: Các câu văn bổ trợ cho câu chủ đề - là sự giải trình, dẫn chững, tái khảng định, hay thêm thông cho câu chủ đề, hay chủ đề. 2.3. Closing Sentence: Câu kết – là tóm lược lại hay tái khảng định lại chủ đề. II. How to Write a Paragraph: Kĩ năng viết một đoạn văn 1. Prewriting Paragraphs: Chuẩn bị trước khi viết The prewriting stage is when you think carefully and organize your ideas for your paragraph before you begin writing. Là quá trình ta động não suy nghĩ, tìm và sắp xếp các ý tưởng cho đoạn văn sẽ được viết. quá trình này tuân theo 6 bước cơ bản sau: Six Prewriting Steps: 6 bước chuẩn bị viết một đoạn văn: Step 1. Think carefully about what you are going to write. Hãy tự hỏi các câu hỏi: What question am I going to answer in this paragraph or essay? How can I best answer this question? What is the most important part of my answer? How can I make an introductory sentence (or thesis statement) from the most important part of my answer? What facts or ideas can I use to support my introductory sentence? How can I make this paragraph or essay interesting? Do I need more facts on this topic? Where can I find more facts on this topic? Step 2. Open your notebook. Hãy trả lời cho các câu hỏi ở bước 1. Không cần phải sử dụng quá nhiều thời gian để thực hiện bước này, thay vì thế hãy liệt kê những ý tưởng quan trọng (2-3 ý chính). Step 3. Collect facts related to your paragraph or essay topic. Tìm và liệt kê các ý tưởng sẽ giúp bạn trả lời các câu hỏi và là ý cho bài viết, hãy chắc chắn rằng những điều bạn liệt kê ra trùng khớp hoàn toàn với chủ đề được yêu cầu. Step 4. Write down your own ideas. Để viết các ý chính hãy tự hỏi các câu hỏi sau: What else do I want to say about this topic? Why should people be interested in this topic? Why is this topic important? Step 5. Find the main idea of your paragraph. Hãy chọn câu chủ đề cho đoạn văn, viết câu chủ đề một cách hoàn chỉnh. Step 6. Organize your facts and ideas in a way that develops your main idea. Sắp xếp các ý, các giải trình, ví dụ, hay những ý kiến bổ trợ sao cho hợp logic, khoa học, chú ý cách dùng từ ngữ, các cụm từ, liên từ (tránh lặp lại các từ đã dùng). 2. Writing Paragraphs: Kĩ năng viết đoạn văn 2.1. Writing process: Tiến hành viết Đây là bước chuyển hóa từ các ý tưởng (đã làm ở phần chuẩn bị trên đây) thành một bài viết hoàn chỉnh (sản phẩm cuối cùng). Tuân thủ 5 bước sau: Five Writing Steps: 1. Open your notebook and word processor. 2. Write the topic sentence, supporting sentences, and closing sentence. 3. Write clear and simple sentences to express your meaning. 4. Focus on the main idea of your paragraph. 5. Use the dictionary to help you find additional words to express your ideas. 2.2. Editing Paragraphs: Sửa lỗi bài viết gồm 2 bước sau: a. Grammar and Spelling: Chữa các lỗi ngữ pháp và chính tả 1. Check your spelling. 2. Check your grammar. 3. Read your essay again. 4. Make sure each sentence has a subject. 5. See if your subjects and verbs agree with each other. 6. Check the verb tenses of each sentence. 7. Make sure that each sentence makes sense. b. Style and Organization: Chữa các lỗi về hành văn 1. Make sure your paragraph has a topic sentence. 2. Make sure your supporting sentences focus on the main idea. 3. Make sure you have a closing sentence. 4. Check that all your sentences focus on the main idea. 5. See if your paragraph is interesting. 3. Useful expressions: Những liên từ, hay các cụm từ hữu ích khi viết đoạn văn: Useful expressions Sequencing/ Listing First of all, First(ly), Initially, To begin with; Second(ly); Third(ly); Next; Then; After that (this); Following this (that); Finally; The first reason is/ The second is; Last but not least Adding to what you have said Also, Furthermore, In addition, Additionally, Moreover, Besides, As well as, Similarly, not onlybut also, even beside this/ that Contrasting In contrast to this, On the contrary, In contrast, Conversely, On the other hand, While, Whereas, However, Despite/ In spite of, Although, Even though, Otherwise, Nonetheless Expressing similarity Similarly; Likewise, In the same way Showing results As a result, As a consequence, Consequently, Hence, Thus, Therefore, So Giving examples For example, For instance, In particular, Particularly, That is to say, Namely, Such as Restating In other words, That is to say, To put it simply Inferring In other words, In that case, or else, Otherwise Summarizing In summary, To sum up, To conclude, To recapitulate, In conclusion, In short, In brief, In a nutshell, Lastly, Finally III. Kinds of Paragraphs: Các loại đoạn văn cơ bản 1. Definition Paragraph: Đoạn văn để định nghĩa về một sự vật, hiện tượng. e.g. Write a paragraph giving the definition of a pest. 2. Classification Paragraph: Đoạn văn để nhóm, hay phân loại các sự vật, hiện tượng. e.g. Write a paragraph discussing two types of energy resources. 3. Description Paragraph: Đoạn văn miêu tả về một sự vật, hiện tượng. e.g. Write a paragraph to talk about your most favorite subject. 4. Compare and Contrast Paragraph: Đoạn văn đề diễn tả sự so sanh hay tương phản về các sự vật, hiện tượng. e.g. Write a paragraph comparing the weather in Vancouver and Halifax. 5. Sequence Paragraph: Đoạn văn mô tả một chuỗi, hay một tiến trình ủa sự vật, sự việc. e.g. Write a paragraph outlining how a person becomes the prime minister. 6. Choice Paragraph: Đoạn văn mô tả sự chọn lựa. e.g. Write a paragraph stating whether you would prefer to play hockey or lacrosse. 7. Explanation Paragraph: Đoạn văn để giải thích e.g. Write a paragraph explaining why so many Europeans moved to Canada during the nineteenth century. 8. Evaluation Paragraph: Đoạn văn để đánh gia về sự vật, hiện tượng. e.g. Write a paragraph evaluating whether pesticides should be used on farms. BÀI 6. EXERCISES ON A-PARAGRAPH-WRITING BÀI TẬP THỰC HÀNH VIẾT ĐOẠN VĂN Exercise 1: In about 140 words, write a paragraph about the kind of job you would like to do after you finish your education. Exercise 2: In about 140 words, write a paragraph about the benefits of reading books. Write your paragraph on your answer sheet. The following prompts might be helpful to you. - Widening knowledge - Improving language - Relaxing. Exercise 3: With around 140 words, write a paragraph to describe a person you admire most. Your writing should include: Who the person is? Why you admire him or her? How he/she affects your life and work? Exercise 4: With around 140 words, write a paragraph giving your opinions of the topic “what makes a person successful in life.” Your writing should include: What success is? The main factors that make people success? How you think about success? Exercise 5: With around 140 words, write a paragraph giving your opinions of the benefits of being able to use English. Your writing should include: What the main benefits of being able to use English? What the examples to illustrate your ideas? Your love for English? Exercise 6: With around 140 words, write a paragraph to describe your homeland. Your writing should include: What your homeland is like? What the main features of your homeland are? How you love your homeland? Exercise 7: With around 140 words, write a paragraph to talk about your favorite school subject. Your writing should include: What your favorite school subject is? Why the subject interests you? How well you learn that subject? Exercise 8: With around 140 words, write a paragraph giving your opinions on the idea of controlling the access to electronic services. Your writing should include: How the electronic services affect people’s life? Why the access to electronic services should be controlled? How people control the access to electronic services? Exercise 9: With around 140 words, write a paragraph giving your opinions about the formal school education system in Vietnam. Your writing should include: How many stages there are? The students’ ages, the length of each stage, the examination if there is? The tuition fee or other requirements? Exercise 10: With around 140 words, write a paragraph giving your opinions on the benefits of working for an International Organization. Your writing should include: How your life will be like when working for an International Organization? Why you choose to work overseas? How you realize your dreams? Exercise 11: In about 140 words, write a paragraph to talk about the kind of job you would like to do after you finish your education. Your writing should include: How your life will be like when working for an International Organization? Why you choose to work overseas? How you realize your dreams? Exercise 12: With around 140 words, write a paragraph giving your solutions to protect the endangered species. Your writing should include: What are endangered species? What are the threats to the endangered species? What are your solutions? THE END Duyệt của Lãnh đạo trường THPT Thái Hòa Lập Thạch, tháng 11 năm 2015 Người soạn và giảng dạy Đỗ Văn Bình
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 GIAO_AN_CHUYEN_DE.docx
GIAO_AN_CHUYEN_DE.docx





